The time has come to take advantage of the latest wide bandgap semiconductor technology with Future Electronics
Wide bandgap semiconductor technology is enabling power-system designers to find new ways to improve their products’ features while reducing system cost. It is no wonder that interest in gallium nitride (GaN) and silicon carbide (SiC) power components is surging.
This product selector guide from Future Electronics gives you all the information you need to start your journey into the wide bandgap semiconductor world.
You can find answers to many of the questions that power designers ask when using GaN or SiC components for the first time, and we have listed the ideal GaN and SiC transistors and drivers from three leading manufacturers: Infineon, onsemi and STMicroelectronics.
Whatever stage you are at – investigating the technology, evaluating components, designing your circuit, or going into volume production – Future Electronics stands ready to help with technical support, product sales, and advanced logistics and manufacturing support services.

What is wide bandgap semiconductor technology?
The term ‘bandgap’ refers to the energy required to move an electron from its outer shell, so that it can move freely. Because of their wide bandgap, SiC and GaN devices can withstand larger electric fields and temperatures than equivalent silicon devices.
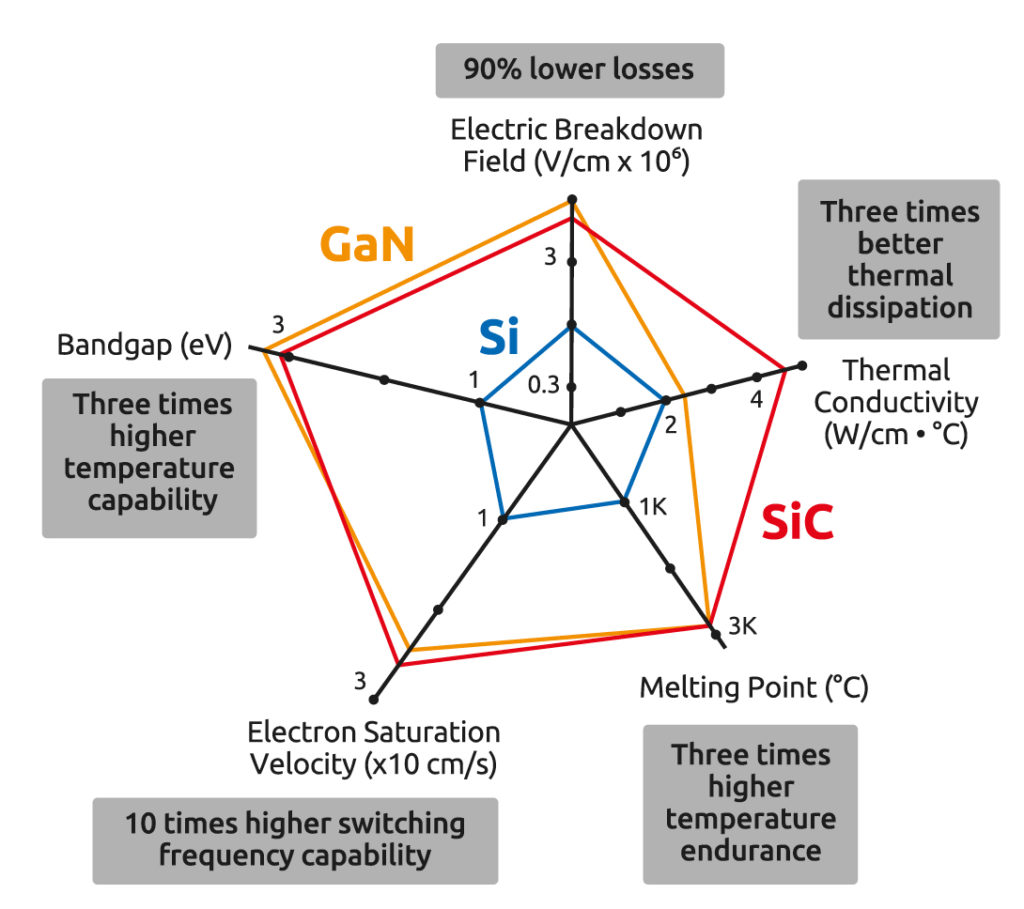
As a result, the values of the resistors and capacitors in the devices can be substantially reduced, shrinking the device’s circuitry, and resulting in faster switching, higher efficiency, and higher robustness, while maintaining an equal or higher blocking voltage rating.
Related: How to Drive the Gate of Wide Bandgap Semiconductors (Digital Future Technology Magazine article)
What are some key advantages of wide bandgap?
Experienced power system designers have found a general rule applies to calculating the value of replacing silicon MOSFETs or IGBTs in a power system with SiC MOSFETs or GaN high electron-mobility transistors (HEMTs):
- Reduce the size (volume) of the system by 50% and maintain the same power output
- Or maintain the same dimensions, and double the power output
GaN and SiC power components switch at higher speed than silicon transistors, have much lower switching losses, and tolerate higher operating frequencies.
This means power systems can use smaller capacitors, inductors and heat sinks, which reduces size, weight and bill-of-materials cost – a win-win-win scenario!

What are some key end products of wide bandgap technology?
- Electric vehicles are heavy users of SiC MOSFETs in on-board chargers and in charging points
- Servers for data centres and telecoms network infrastructure use GaN HEMTs and SiC MOSFETs for high efficiency, to reduce energy consumption and operating costs
- Industrial power supplies use SiC MOSFETs and GaN HEMTs because they enable higher efficiency and reduced size, and can handle high-temperature operation
- Power system designers are miniaturizing chargers for smartphones and laptops by replacing silicon MOSFETs with GaN HEMTs

Related: DC Fast EV Charging with onsemi
When should I use Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Gallium Nitride (GaN)?
Practical experience of using SiC MOSFETs and GaN HEMTs in commercial products has revealed the ideal application conditions for each technology.
For power systems supplying up to 1 kW, the best choice is GaN technology.
Compact systems such as USB Type-C® chargers use integrated products which combine the HEMT and driver in one package – the Master GaN products from STMicroelectronics or CoolGaN™ IPS from Infineon are good examples.
For power systems supplying up to 2 kW, SiC MOSFETs are widely used today. But the latest GaN HEMTs are suitable for use up to 2 kW. The Future Electronics GaNdalf PFC board, rated for loads up to 2 kW, uses Infineon CoolGaN™ HEMTs.
For power systems supplying more than 2 kW, SiC MOSFETs are the right choice. SiC devices are available with breakdown voltage ratings from 650 V up to 1,700 V. The maximum voltage rating for GaN HEMTs is 650 V.
Transform your power system design!
Future Electronics has developed a range of development boards to enable customers to evaluate wide bandgap semiconductor technology in realistic application scenarios.
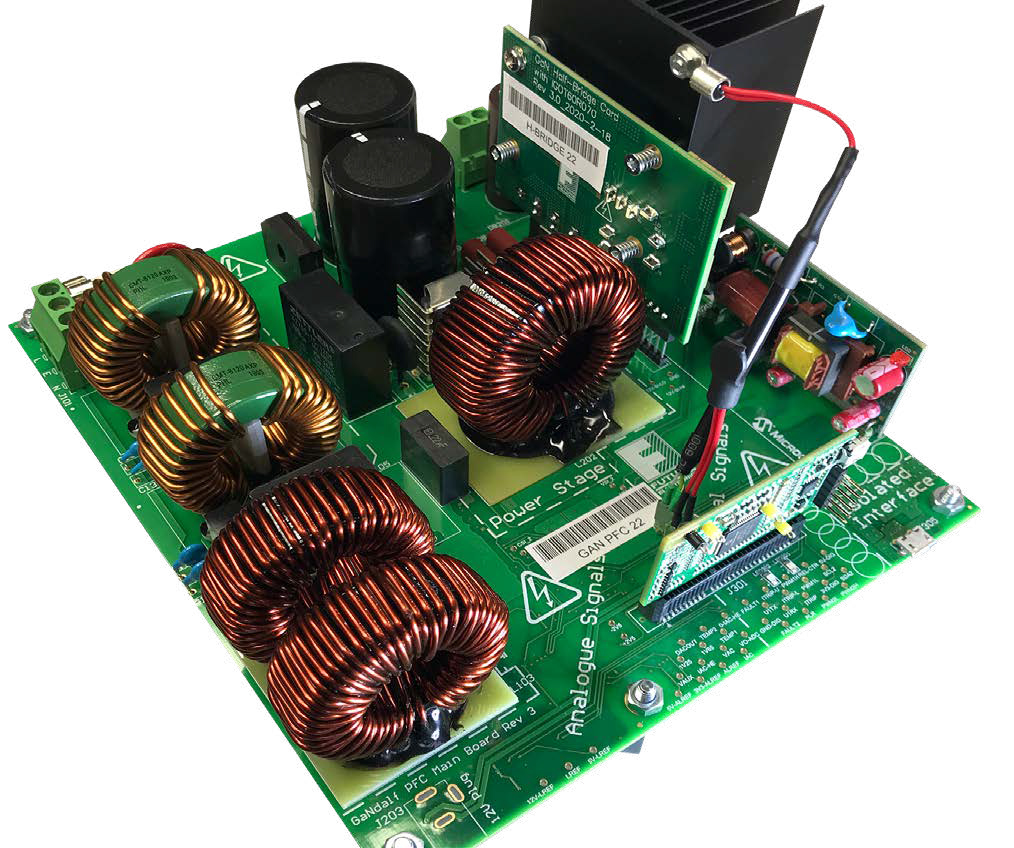
GaNdalf II
GaNdalf II is a 2 kW PFC system which uses Infineon CoolGaN™ power switches to implement a bridgeless totem pole hard-switching topology. The GaNdalf II board achieves peak efficiency higher than 99%, and power factor of >0.99. GaNdalf is also available with SiC MOSFETs from several vendors like Infineon, onsemi and STMicroelectronics.
TobogGaN
TobogGaN is a reference design system for industrial and telecoms auxiliary power supplies rated for loads up to 60 W. Using GaN power switches, the TobogGaN board offers efficiency up to 92%, as well as very high power density.

The best of the wide bandgap semiconductor world, only from Future Electronics
The best products
The superior properties of gallium nitride and silicon carbide semiconductors in power systems were discovered many years ago. But it took the applied expertise of the world’s leading semiconductor manufacturers to develop commercial GaN and SiC products which were suitable for volume production.
Three of these wide bandgap pioneers – Infineon, onsemi and STMicroelectronics – today offer the industry’s widest portfolio of GaN HEMTs, SiC MOSFETs, dedicated drivers, and integrated GaN-based power converters. All three companies’ products are in stock and available to buy from Future Electronics.
The best technical support and advice
Future Electronics’ power specialist field applications engineers are highly knowledgeable about the product options and design considerations involved in implementing wide bandgap semiconductor technology. Based in branches all over Europe, the FAEs are ready to help with every aspect of using SiC or GaN transistors.
They are backed by the Future Electronics Power Systems Centre of Excellence in London, which has built various GaN and SiC transistor-based systems for customers, and can draw on this experience when advising on customers’ design projects.
The best product information
This Product Selector Guide provides up-to-the-minute information about the best and newest SiC and GaN components. Future Electronics customers can also subscribe to FTM, the industry’s best product news magazine, which regularly features new wide bandgap semiconductors.
Product pricing and availability can be found 24/7 at www.FutureElectronics.com.
More questions? We have answers
The advantage of wide bandgap semiconductors is that supporting components such as the heatsink and magnetics are smaller and lighter than in an equivalent silicon switch-based design. Wide bandgap devices can support the use of new power topologies, such as the bridgeless totem pole arrangement for PFC designs. Power controllers which implement these new topologies are available from Future Electronics, alongside every other supporting component for a high-efficiency power conversion circuit.
First-generation SiC and GaN devices required the application of extensive counter-measures to combat common-mode noise. But the SiC and GaN products supplied today by Infineon, onsemi and STMicroelectronics generate no more noise problems than silicon MOSFETs or IGBTs do, thanks to innovations in packaging such as top-side cooling and the addition of an extra Source pin.
The leading manufacturers of SiC and GaN devices have been investing heavily in production capacity since the mid-2010s. In the late 2010s, supply was limited because the car industry soaked up most of the available inventory, but production has been ramped up so much since then that products are now available to customers in all market sectors, with lead times similar to those of silicon power ICs.
In principle, a SiC MOSFET or GaN HEMT operates in a similar way to any other power switch. The most important difference is in the design of the transformer. At the high switching frequencies which SiC and GaN devices support – sometimes higher than 250 kHz – a transformer used in a low-frequency design would encounter skin effects and proximity losses, substantially reducing system efficiency. A custom transformer can be optimized for high-frequency operation and high efficiency. Future Electronics’ power specialists can help customers with their transformer design.






