As we continue to dive into the market to provide you with insights, trends, and opportunities for business and innovation, one of the most favored topics has been energy storage. Power electronics-based energy storage technologies are increasingly gaining relevance due to their key role facilitating the accessibility of renewable energy sources, improving grid stability and reliability, and decentralization of energy generation.
This emerging sector of the industry has been valued at around US$ 210 billion in 2021 and is expected to grow to around US$ 400 billion for 2030.
Why is energy storage vital today, why you might be interested in adding it to your innovation agenda, and where do your ideas fit in the picture? Follow this article to get a glimpse of the future.
In this article:
What are Energy Storage Systems?
4 key drivers for Energy Storage Systems
Before the meter and behind the meter applications
Energy Storage Sector: State of the Art
5 Application Trends for the Energy Storage Systems Sector
What are Energy Storage Systems?
Energy Storage Systems (ESS), in broad terms, are the systems that store energy during times when it is abundant and release it when it is needed. Energy storage systems are a trending topic for energy innovation in 2023 as they facilitate the integration of renewable energy source, promote the decentralization of the electrical grid, and are crucial for devices that are becoming standard for consumers, such as portable electronic devices and e-mobility.
Energy storage comes in many shapes and sizes. Depending on the application, innovations, and availability, different types of energy storage technologies are currently available. Some examples include:
- Batteries
- Pumped hydro storage
- Flywheels
- Compressed air energy storage
- Thermal energy storage
- Hydrogen storage
Energy Storage Systems are becoming increasingly important as the world transitions to a more sustainable energy future. Innovation in Energy Storage Systems can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve grid stability and reliability, and increase energy access and security.
Why is this?
Energy storage is crucial for the further development of renewable energy sources and the decentralization of energy generation because it helps to address the inherent intermittency of these sources, manage peak demand, improve grid stability and reliability, and facilitate the integration of small-scale renewable energy systems into the grid.
- Intermittency of renewable energy sources: Renewable energy sources are inherently intermittent, meaning that they are not constantly generating energy, but depend on the availability of natural resources like the sun and wind. Energy storage makes it possible for excess energy to be stored when it’s highly available in peak production hours, to later be released when it’s needed, thereby smoothing out the variability of these energy sources.
- Managing peak demand: Similarly, but on the other side, energy storage can help to manage peak demand by storing excess energy during off-peak hours and releasing it during times of high demand. This can reduce the need for additional generating capacity and help to avoid blackouts and brownouts.
- Grid stability and reliability: Energy storage can also improve grid stability and reliability by providing backup power during outages and balancing the supply and demand of energy.
- Decentralization of energy generation: Energy storage can facilitate the decentralization of energy generation by allowing small-scale renewable energy systems, such as rooftop solar panels, to store excess energy and feed it back into the grid when needed. This can increase energy independence and facilitate smart grids.
RELATED ARTICLES: Smart grid and smart meter: business trends and opportunities

4 key drivers for Energy Storage Systems
- Renewable energy integration: The increasing use of renewable energy sources is a major driver for energy storage systems. Given the intermittent nature of renewable energy sources, energy storage systems become key to help store excess energy during times of high generation and release it when needed, making renewable energy more reliable and consistent.
- Grid modernization: Aging infrastructure and growing demand for electricity are driving the need for grid modernization. Energy storage systems can help to improve the reliability and stability of the grid, reduce the need for new power plants, and support the integration of distributed energy resources as well as the decentralization of production.
- Energy independence: Energy storage systems can help empower consumers and gain independence as they provide backup power during outages, reduce reliance on the grid.
- Environmental concerns: The need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change is driving the growth of renewable energy sources and energy storage systems. Integration and innovation in this sector can help battle the race to reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and promote a more sustainable energy future.
Before the meter and behind the meter applications
Definitions
“Before the meter” refers to energy systems that are located on the utility side of the electric meter, meaning that they are owned and operated by the utility company. Examples of before the meter systems include conventional and renewable energies with stationary ESS, bulk storage, substation, utility wind & utility photovoltaic
On the other hand, “behind the meter” refers to energy systems that are located on the customer’s side of the electric meter, meaning that they are owned and operated by the customer. Examples of behind the meter systems include rooftop solar panels (PV), charging stations, energy storage systems, and backup generators.
Benefits of ESS in before-the-meter applications
- Grid reliability and stability
- Transmission capacity/peak period transmission management and optimization
- Intermittent renewables: smooth out weather-dependent sources of energy.
Benefits of ESS in behind-the-meter applications
- Excess, unused energy generated by commercial and residential PV is stored in batteries and readily available for later consumption.
- EVs require low-cost reliability ESS for commercial and residential charging stations. As EVs become more standardized, residential ESS becomes essential.
Energy Storage Sector: State of the Art
Current groups of interest and stakeholders
- Inverter manufacturers: These companies are currently focusing on innovation of renewable energy. Inverter manufacturers (mostly) will purchase batteries from other sources to continue to focus on the development of inverters and electrical components.
- Battery manufacturers: Their expertise is in battery management and technology; however, battery manufacturers could be addressed for inverter technology and power needs.
- Big solution provides: While a wide range industrial companies are most likely already present in grid applications, the focus on energy storage has been low until now. However, their existing presence and combination of relevant expertise can be an asset to the creation of energy storage systems.
- Dedicated solution providers: Companies dedicated exclusively to energy storage are mostly small, newer companies that rely on distribution and residential applications, but possess large potential for growth and collaboration.
Regional penetration
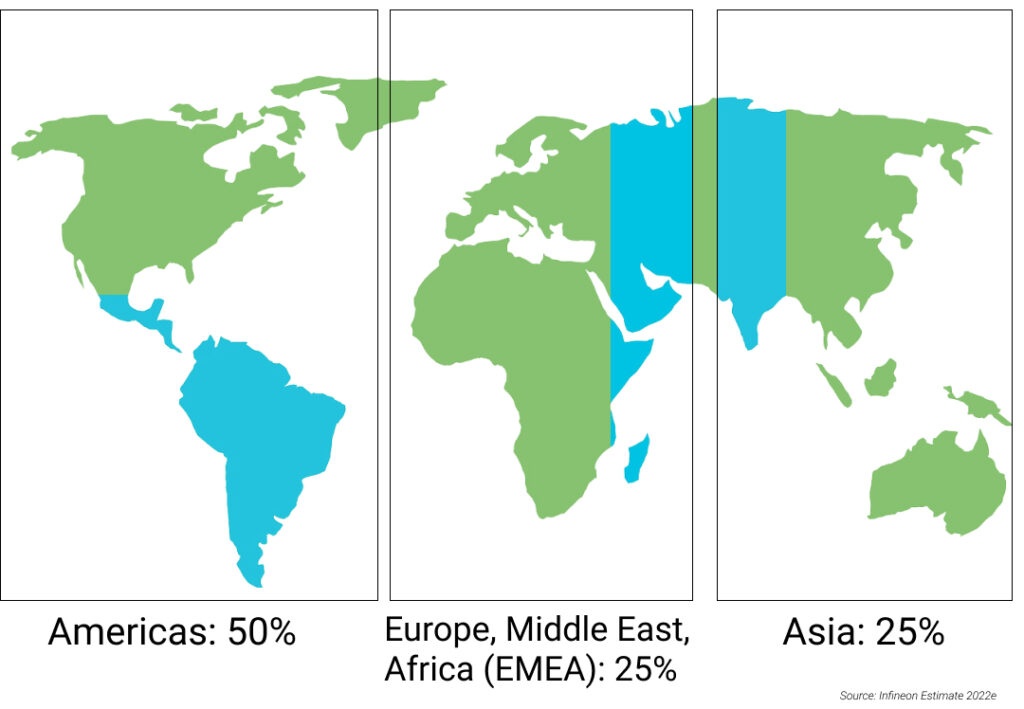
- Americas: 50%
- Europe, Middle East, Africa (EMEA): 25%
- Asia: 25%
5 Application Trends for the Energy Storage Systems Sector
- Lithium-Ion: Plummeting costs, advanced batteries, and alternatives
In 2010, the cost of lithium-ion batteries was around $1,100 per kilowatt-hour (kWh). By 2020, the cost had fallen to around $137 per kWh, representing an 89% decline in just ten years. This trend is expected to continue, with some industry experts predicting that the cost of lithium-ion batteries could fall to as low as $60 per kWh by 2030. The plummeting costs of lithium-ion batteries have made energy storage systems more cost-competitive with traditional grid infrastructure and have contributed to the growth of the energy storage industry. As the cost of lithium-ion batteries continues to decline, we can expect to see even greater adoption of energy storage systems
Yes, but….
While Lithium-Ion batteries have proven benefits like high energy density, long cycle life, low self-discharge rate, fast charging time, and widespread availability and established market… they come with their own downsides. Some of which are the limited raw material availability, risk of overheating and flammability, and environmental concerns related to extraction and disposal.
This concerns have also paved the way for the second major trend we have spotted for Energy Storage Systems
- Alternative battery technologies
As the trends continue to focus more on cleaner energies and safer alternatives, innovation for battery technology becomes a huge area of opportunity. With that in mind, we can already spot a couple recurring topics that are worth exploring for the future.
- Solid-state batteries: these use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, which can lead to higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety.
- Redox Flow batteries: these store energy in external tanks containing electrolytes, allowing for greater scalability and longer cycle life.
- Sodium-ion batteries: these use sodium ions instead of lithium ions, which are more abundant and cheaper to extract, although they have lower energy density and are less mature than lithium-ion batteries. E-mobility
- Energy Storage as a Service (ESaaS)
ESaaS providers install and operate the energy storage systems on behalf of customers, who pay a monthly or annual fee for the service. This allows customers to benefit from the advantages of energy storage without the upfront capital investment or ongoing maintenance costs associated with owning and operating the systems. ESaaS providers may also offer additional services such as energy management and optimization to further enhance the value proposition for customers. The ESaaS model is gaining traction in various markets, including commercial and industrial, residential, and utility-scale applications, and is expected to continue to grow as the energy storage market expands.
- Portable Electronic Devices
The energy density, cycle life, and charging time of batteries are key factors that determine the performance and user experience of portable electronic devices. The development of new battery chemistries promises to deliver improvements in these areas, resulting in a wide range of innovation possibilities as Portable Electronic Devices become more and more a part of our daily lives as consumers.
- E-mobility
EVs rely on rechargeable batteries to store energy and power their electric motors. The energy density, charging time, and lifespan of these batteries are crucial factors that affect the performance, range, and durability of EVs. Energy storage solutions are also necessary for the deployment of charging infrastructure, including fast-charging stations, which require large amounts of power in short periods of time. Energy storage can help to mitigate the variability and intermittency of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, which can be integrated into the EV charging ecosystem to further reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency. As the EV market continues to grow, advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and energy management systems will be essential to further improve the performance and affordability of EVs and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.
In Conclusion…
Energy storage systems are essential for the further development of renewable energy sources and the decentralization of energy generation. As technology continues to improve and costs continue to decline, energy storage is poised to play an increasingly important role in the transition to a more sustainable and resilient energy system.
How can your ideas enter the market and make a difference in the future?






