The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT) is quickly becoming as important to the healthcare industry as the regular internet has become to pretty much everything. But what is it and what are some examples of applications?
In this article
- IoMT: The next electronic engineering revolution and its featured devices
- But what exactly is IoMT?
- The medical industry before and after IoMT
- 5 IoMT examples and applications
- Conclusion and what’s in the future for IoMT
With a trend for most global healthcare organizations implementing IoMT solutions, and considering the 2020 health crisis, IoMT market size skyrocketed to over 41 billion dollars by 2020 and is estimated to reach USD 176.82 billion by 2026. As the numbers keep growing, and technology keeps improving, the Internet of Medical Things is a topic of interest for engineers, doctors, and potential users alike.
What exactly is IoMT?
IoMT is, basically, bringing the logic behind Internet of Things (IoT) technology into the healthcare industry. It’s the interconnected network of information travelling through everyday devices used for medical purposes. IoMT is the seamless interaction between the digital and the physical world in a web of growing data provided by our day-to-day interaction with devices.
Imagine, for example, a hospital bed that senses when a patient is trying to get up. Or connecting the information from a blood pressure or heart rate monitor with a remote device that can send notifications in case of emergency. Imagine getting remote medical follow-up throughout the information gathered in these devices. IoMT applications are limitless, and it is definitely more, a lot more than Zoom calls with your doctor.
How has the medical industry changed before and after IoMT?
The medical industry has seen its share of milestone revolutions. The first one was possibly hand-washing protocols. The latest: IoMT.
There’s no need to go over the fatal crisis we all went over in 2020. Thankfully, we can only imagine how much worse it could’ve been if some basic internet technology wasn’t available. For example, online applications and conference calls allowed thousands of people to report their symptoms or meet with doctors online.
However, more in-depth dedicated IoMT technology has been changing the lives of patients for years. Wearable devices, such as glucose control monitors, have saved millions of valuable hours for diabetes patients and doctors, making follow-up meetings way less frequent and much more efficient. In cases of emergency, these monitors can even save their lives by being a preventive force and a quick medium to reach the doctor. This type of patient-monitoring devices attend a variety of patient needs. While a wide range is currently available, as technology evolves, these devices continue to be developed and improved.
Further than personal patient devices, IoMT technology is becoming a staple in hospitals across the world. From relatively simple temperature and humidity sensors that provide optimal conditions for patients or equipment, to what are now being referred to as Smart hospitals, which take full advantage of IoMT through their every process, from inventory and asset management to in-clinic devices and remote care systems.
However simple or complex, the adoption of IoMT is quicky becoming the norm in healthcare globally. The following are some examples of the devices that have changed or promise to change our everyday interactions with the healthcare industry.
What are some IoMT applications?
Patient wearable monitors
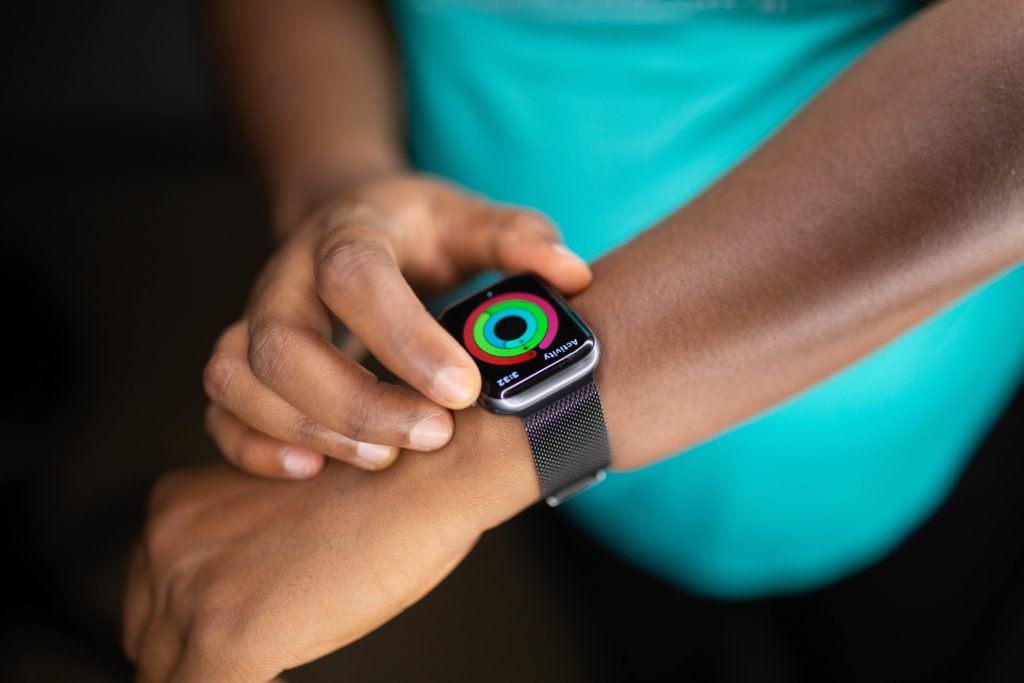

Wearable healthcare technology comprehends all electronic devices from heart monitors to smartwatches that can be worn almost (or exactly) like an accessory for the patient. Wearable devices are the ultimate case for portability. Their capacity to track important health indicators, along with their connectivity, can reduce the need for follow-up appointments with doctors and even alert and prevent possible emergencies. Thanks to their almost attached nature, these devices make it easy for patients to have a constant reminder, motivation, or consciousness of any habits they must track, be it standing up to stretch, going for a walk, taking a medicine, eating certain foods at certain times, or even when it’s time to go see a professional.
Patient wearable devices have been around for a while, and with the rise of smartwatches, they’re more common every day. Through connectivity, IoMT, and the quick technological improvements of today, the future of wearable healthcare is potentially infinite. Here are some examples that have changed millions of lives to date.
Heart rate / ECG monitors
Monitoring heart health used to be a challenging process, since many rapid fluctuations went unseen if not through a doctor’s appointment and with the necessary healthcare facilities. With wearable technology, heart rate and ECG monitors are at the palm of the hand – or the wrist – of the patient. This keeps continuous track of the patients’ heart health and can measure (depending on the device) from electrocardiograms to daily steps, physical activity, elevation, and more.
Glucose monitors
Personal, wearable glucose monitors are changing the lives of the millions of diabetes patients who were previously challenged with manual glucose level tests. In addition to the inconvenience of traditional testing, the patients and doctors were limited to the information delivered only at the time of testing. With wearable glucose monitors, patients can have continuous tracking, receive alerts and notifications when something is needed, and keep automatic record of the patient’s wellbeing through the periods of time between visits to the doctor.
Other examples of conditions that can be tracked through wearable devices include:
- Depression and mood monitoring
- Parkinson’s disease monitoring
- Blood pressure monitoring
- Fitness trackers
How are healthcare workers utilizing IoMT?
IoMT devices are not only making lives easier for patients, but for healthcare workers as well. Being able to monitor patients remotely, for example, can save a lot of trouble for doctors who have the information readily available through software that will often analyze some data for them. Not only is the data easier to access, but it’s more precise too, since as we saw earlier, there’s more to work with than only the tests that can be run during in-person appointments. Even more so, in a crisis, remote interactions with your doctor can be hugely impacted when the information is precise without the need to commute to the facilities.
IoMT for healthcare professionals can also impact the healthcare facilities themselves. Some examples are the digital transformations that are overtaking hospitals and turning them into smart hospitals. This, as we saw earlier, can go from temperature sensing technology to asset management software. Another specific case could be the hand-hygiene monitoring system implemented that helped reduce infections by more than 60% within some hospitals. This technology worked by simply identifying when staff entered a room and then reminding them to sanitize their hands. This system, of course, faced the limitation of only being able to remind staff, and not actually sanitizing their hands for them. Still, the results were impressive… and who knows in the future… we’ve seen technology do crazier things than wash our hands!
Connected devices

By definition, all IoT devices must be connected in some way. That’s what the internet is… an interconnected network. What this category tries to highlight are those traditional devices that were used for specific patient purposes or conditions, and that are now equipped with IoT technologies. For example, connected inhalers for patients with asthma or COPD are used as regular inhalers, but keep track of the frequency of attacks and some environmental data that could help healthcare professionals analyze the situations and environments in which these events happen.
Ingestible sensors

Sensors help healthcare workers collect data from patients. However, sometimes the data required comes from inside the patient’s body. For many years, the only way to retrieve some of this data was through complicated and uncomfortable procedures like inserting cameras or probes through the patient’s digestive system. Nevertheless, the increased precision, connectivity and reduced size of newer sensors has allowed the med tech industry to develop ingestible sensors that can pinpoint certain indicators like stomach PH levels or sources of bleeding. These pill-sized sensors are designed to fulfill their purpose as they pass through or dissolve naturally through the patient’s body. While their use and development is still in the early stages, the potential is, as with all med tech and IoMT, as great as our imagination.
Robotic surgery
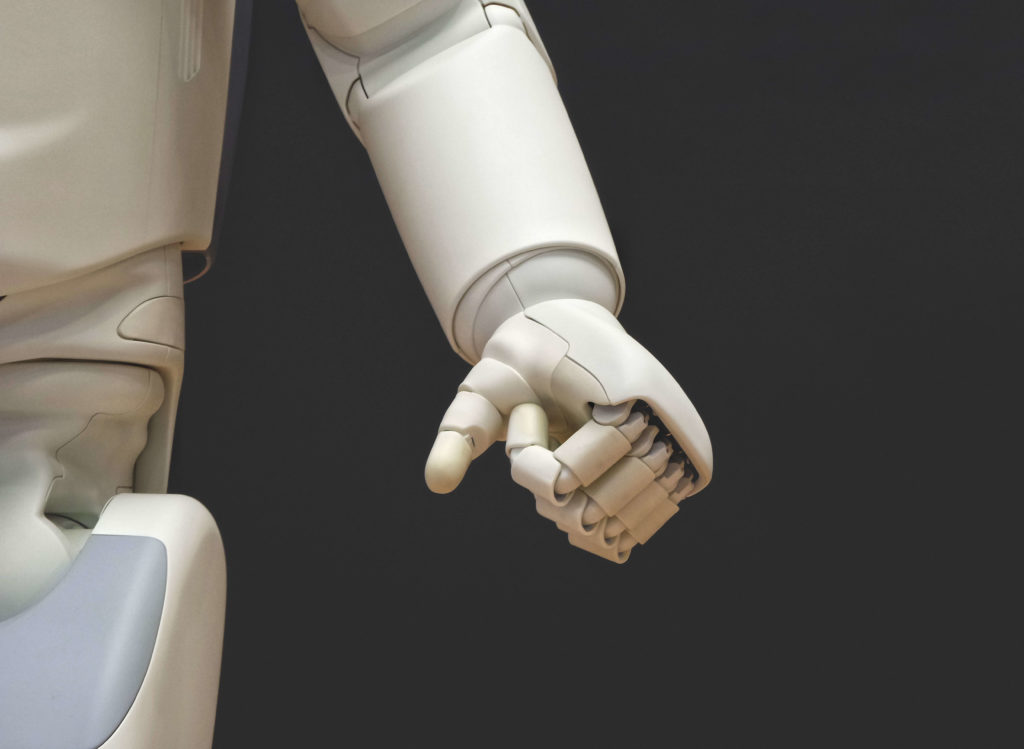

Robotic surgery is perhaps one of those terms that makes us feel like we’re living in the future. While robot-assisted surgery has been around for some years, the latest innovations in med tech have launched tiny IoMT connected robots or drones that can be controlled by surgeons to perform surgery on patients. These robots can easily access areas and perform tasks that would be difficult for human hands. In addition, robotic surgery procedures are much less invasive and require dramatically smaller incisions in the patient’s body, leading to even faster recovery and healing.
What is the future for IoMT?
IoMT is the next big step in med tech and the healthcare industry. Its potential and ideas for the future are seemingly limitless… some existing patents include connected contact lenses that could keep track of what your eyes see through the day!
With engineers, scientists, and designers coming up with new ideas every day, and with the exponential growth of technology, AI, and machine learning, the future of IoMT looks optimistic. And with an optimistic look for IoMT comes an optimistic outlook for every potential patient’s quality of life.
Header photo by Jair Lázaro on Unsplash






